Collagen, Research Reagent (Liquid)
Characteristics of Collagen Classified Based on Its Molecular Species and Extraction Methods
◆Collagen type I
Type I collagen is the major fibrous protein in the extracellular matrix. It can be found in most organs, but is particularly abundant in bone, tendon, and dermis.
Acid Soluble Collagen(ASC)
・Due to its high gel strength, this collagen preparation is ideal for both “On-Gel” and “In-Gel (Gel-Embedded)” cultures.
・Filtered through a 0.45 μm pore size membrane.
Pepsin Solubilized Collagen (PSC)
・ Atelocollagen prepared by enzymatically removing telopeptides.
・ This form of collagen has high cellular adhesiveness, making it perfect for coating cell culture vessel surfaces.
・ Filtered through a 0.45 μm pore size membrane.
◆Collagen type Ⅲ
This is a fibrillar collagen abundant in tissues with high elasticity, such as juvenile skin tissues and the arterial tunica media where smooth muscle cells populate. Type III collagen is also expressed during embryogenesis and wound healing.
・Atelocollagen prepared by enzymatically removing telopeptides.
・Filtered through a 0.45 μm pore size membrane.
◆Collagen type Ⅳ
Type IV collagen is one of the major components of basement membranes. It polymerizes to form a mesh-like network in the basal lamina.
・Acid-extracted native collagen.
・This form of collagen has high cellular adhesiveness . It is suitable for collagen-gel cultures and collagen-coating of culture vessel surfaces.
-
Excellent high cellular adhesiveness
Type I collagen promotes cell adhesion more efficiently than BSA.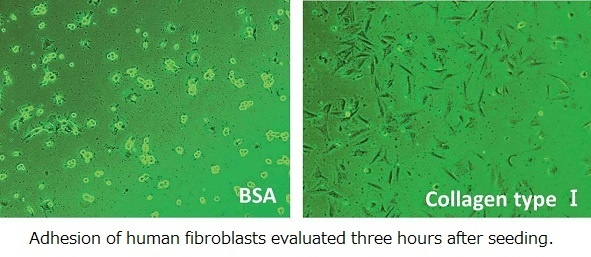
-
Reconstituted Collagen Fibrils
An elaborate fibrillar network was formed following the exposure of collagen molecules to physiological conditions.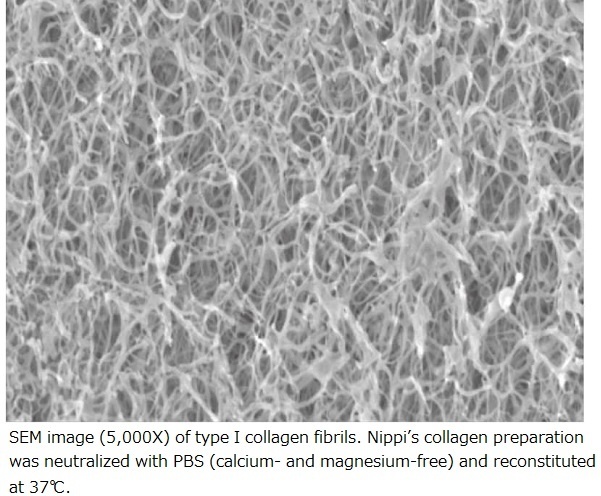
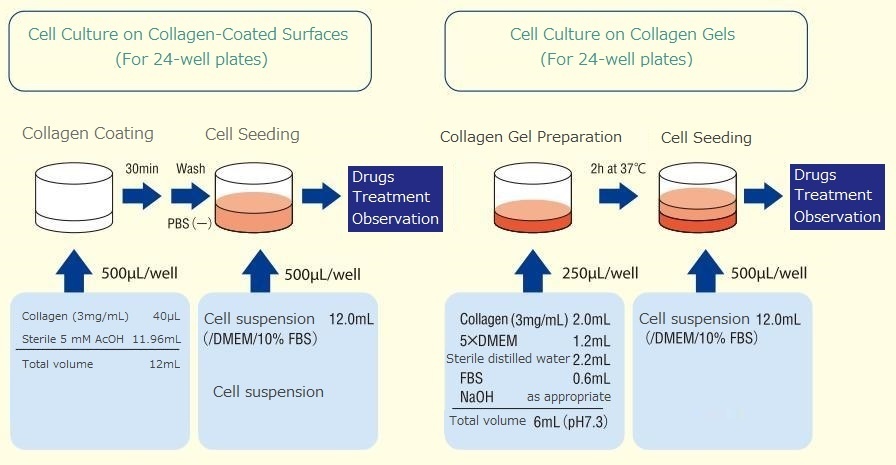
Instructions for Use
Collagen, Research Reagent (Powder)

Collagen has long been available only as either a liquid or lyophilized preparation. Nippi Inc. used its proprietary technology and succeeded in producing easy-to-use collagen powder that maintains the protein's native structure (triple helix). (International patent pending.) You can now prepare a collagen solution at a desired concentration using the solvent of your choice.

Advantages
- Unlike lyophilized or spray-dried products, Nippi’s collagen powder exhibits excellent solubility due to its large surface area (Nippi’s in-house data).
- Allows for the easy adjustment of collagen concentrations in a desir solvent.
- Enables the use of a variety of solvents.
- Retains the native structure (triple helix) of collagen fibrils.
Applications
- Generation of physical supports for 2D and 3D cell cultures.
- Production of molded collagen products.
- Research and development of new drug delivery systems (DDSs).
- This product is NOT sterile.(If you require sterilization solution, please filtration by sterilized filter)
Preparation of Collagen Solution
- Simply dissolve in an appropriate solvent (for example, 5 mM acetic acid or 1 mM hydrochloric acid). However, when preparing highly concentrated collagen solutions, first disperse this product in water, and then add a suitable solvent.
- Collagen solutions can be prepared in a wide range of concentrations. However, high-concentration (≥5 mg/mL) collagen solutions are very viscous and difficult to work with.
- A solution of up to approximately 10 mg/mL can be prepared.
