Phos-tag™ SDS-PAGE can be performed to separate phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated proteins by mixing Phos-tag™Acrylamide with acrylamide solution to allow for polymerization to occur.
Features
- It can be used regardless of the type and position of amino acid residues.
Able to analyze unknown phosphoproteins.
Able to detect new phosphorylation sites for which anti-phospho antibodies are not commercially available. - Phosphorylated forms with different number and location of phosphorylated sites can be separated.
Able to determine the level of phosphorylation and the number of phosphorylated forms. - It can be used to detect phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated forms simultaneously.
Able to quantify each phosphorylated form.
Able to determine the presence of phosphorylation easily. - Radioisotopes and special equipment are not needed.
Experiments can be carried out easily at low costs (Only SDS-PAGE reagents and equipment are required). - After electrophoresis, WB- and MS-based analyses and 2D gel electrophoresis can be performed.
WB: Internal proteins can be analyzed.
MS: The combinations of phosphorylated sites for each phosphorylated form can be determined.
2D gel electrophoresis: Phosphorylated forms with identical isoelectric points or molecular weights can be separated.
User Manual
Principles of Phos-tag™ SDS-PAGE
Structure of Phos-tag™ Acrylamide
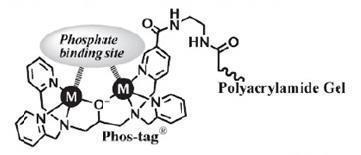
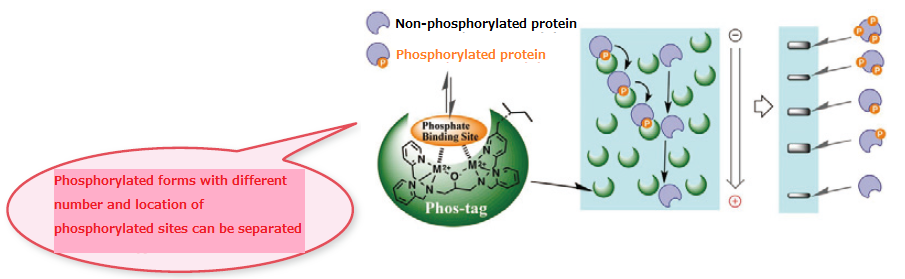
- Two divalent metal ions trap phosphorylated proteins during migration.
- The higher the level of phosphorylation, the slower the migration velocity.
- Separation occurs based on the level of phosphorylation.
(phosphoproteins with the same number of phosphorylation can be separated if the phosphorylation sites are different)
Phosphorylation of substrates cannot be detected with conventional SDS-PAGE (Figure above: without Phos-tag™)
Application: Time Course of α-casein Dephosphorylation
Phos-tag™ SDS-PAGE and conventional SDS-PAGE were performed to separate samples of α-casein, which had been dephosphorylated over time (incubation period: 0-120 mins) by alkaline phosphatase.

Phos-tag™ Webinar
Phos-tag™ is a functional molecule that captures every phosphorylation of proteins such as Ser/ Thr/ Tyr. It has been used widely by many researchers to separate, detect, analyze, and purify phosphorylated proteins.
This webinar entitled “Application of Phos-tag™ to identify protein kinases involved in the phosphorylation of DNA methyltransferase 1” is presented by Prof. Sugiyama of the Faculty of Agriculture, Kagawa University.
