
Collagen and Gelatin- Nippi Inc. products -
Collagen, Research Reagent (Liquid)
Characteristics of Collagen Classified Based on Its Molecular Species and Extraction Methods
◆Collagen type I
Type I collagen is the major fibrous protein in the extracellular matrix. It can be found in most organs, but is particularly abundant in bone, tendon, and dermis.
Acid Soluble Collagen(ASC)
・Due to its high gel strength, this collagen preparation is ideal for both “On-Gel” and “In-Gel (Gel-Embedded)” cultures.
・Filtered through a 0.45 μm pore size membrane.
Pepsin Solubilized Collagen (PSC)
・ Atelocollagen prepared by enzymatically removing telopeptides.
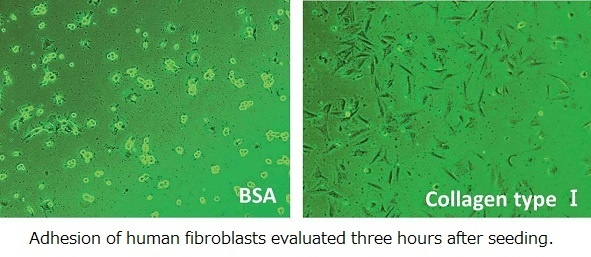
・ This form of collagen has high cellular adhesiveness, making it perfect for coating cell culture vessel surfaces.
・ Filtered through a 0.45 μm pore size membrane.
◆Collagen type Ⅲ
This is a fibrillar collagen abundant in tissues with high elasticity, such as juvenile skin tissues and the arterial tunica media where smooth muscle cells populate. Type III collagen is also expressed during embryogenesis and wound healing.
・Atelocollagen prepared by enzymatically removing telopeptides.
・Filtered through a 0.45 μm pore size membrane.
◆Collagen type Ⅳ
Type IV collagen is one of the major components of basement membranes. It polymerizes to form a mesh-like network in the basal lamina.
・Acid-extracted native collagen.
・This form of collagen has high cellular adhesiveness . It is suitable for collagen-gel cultures and collagen-coating of culture vessel surfaces.