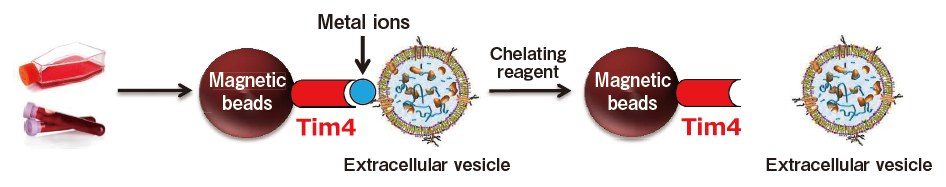
A new method for exosome purification using phosphatidylserine and Tim4
The exosome membrane contains proteins and lipids derived from secretory cells. Among those components, phosphatidylserine (PS) is known to be oriented inside the cell membrane of intact cells by the enzymatic activity of lipid flippase, and be known to be exposed also on the outer surface of exosome membrane3). In addition, T-cell immunoglobulin domain and mucin domain-containing protein 4 (Tim4), the receptor involved in phagocytosis of apoptotic cells by macrophages, is known to bind PS via the IgV domain located within the extracellular region in a calcium ion-dependent manner.4)
Based on these findings, we developed a new and unprecedented method for exosome purification using Tim4-immobilized magnetic beads (capable of capturing exosomes in samples such as culture supernatants and serum in the presence of calcium ions and releasing them by elution with a buffer supplemented with a chelating reagent) in collaboration with Professor Rikinari Hanayama (Department of Immunology, Kanazawa University Graduate School of Medical Sciences) and successfully constructed an exosome purification kit based on these magnetic beads5).
This exosome purification kit, MagCapture™ Exosome Isolation Kit PS, has realized easy purification of intact exosomes with higher purity than that obtained by any conventional methods for exosome purification. It is currently being established as a new exosome purification method replacing ultracentrifugation, the conventional gold standard.
A novel affinity-based method for phosphatidylserine (PS) on the surface of extracellular vesicles
References
- Tkach, M. et al. Communication by Extracellular Vesicles : Where We Are and Where We Need to Go. Cell 164, 1226-1232(2016).
- Raimondo, F. et al. Advances in membranous vesicle and exosome proteomics improving biological understanding and biomarker discovery. Proteomics 11, 709-720(2011).
- Trajkovic, K. et al. Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science 319(5867) : 1244-7(2008).
- Miyanishi, M. et al. Identification of Tim4 as a phosphatidylserine receptor. Nature 450, 435-439(2007).
- Nakai, W. et al. A novel affinity-based method for the isolation of highly purified extracellular vesicles. Sci. Rep. 6, 33935(2016).
MagCapture™ Exosome Isolation Kit PS
-
Novel affinity method
- Isolating by a PS-binding molecule※
- Low background
- Mild elution by a chelating reagent under a neutral pH condition
※High purity exosomes can be easily isolated by PS affinity method.
High purity and intact exosomes
-
No required ultracentrifugation
- Easy operation using magnetic beads
- Optimized protocol

High reproducibility
Comparison with other purification method
| Methods | Exosome purity | Recovery amount | Intact or not | Total Protein yield |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MagCapture™ (PS affinity method) |
■ ■ ■ ■ | ■ ■ ■ | Yes | ■ |
| Ultracentrifugation | ■ ■ | ■ ■ | Yes | ■ ■ ■ |
| Polymer-based precipitation | ■ | ■ ■ | Yes | ■ ■ ■ ■ |
| Density gradient centrifugation method | ■ ■ ■ | ■ | Yes | ■ ■ |
| Size fractionation method | ■ ■ ■ | ■ ■ | Yes | ■ ■ |
| Exosome surface antigen affinity method (using the antibody) |
■ ■ ■ | ■ ■ | No | No data |
※This comparison table is based on our own survey. Since the results vary depending on a sample, a detection target and method, the performance of each method is not guaranteed.
Target samples: cell culture supernatant, serum, plasma, urine, etc.
Preprocessing protocols for various samples
This is the section to prepare samples. When exosomes and other large EVs (microvesicles) are needed, prepare 1,200 x g supernatant ※ 1 as a sample.
Additionally, when highly purified exosomes are needed, prepare 10,000 x g supernatant ※ 2 as a sample. This protocol for sample preparation is set for cell culture medium, serum, and plasma. When other body fluids are used, please examine the appropriate preprocessing protocol by referring to the protocol for serum and plasma.
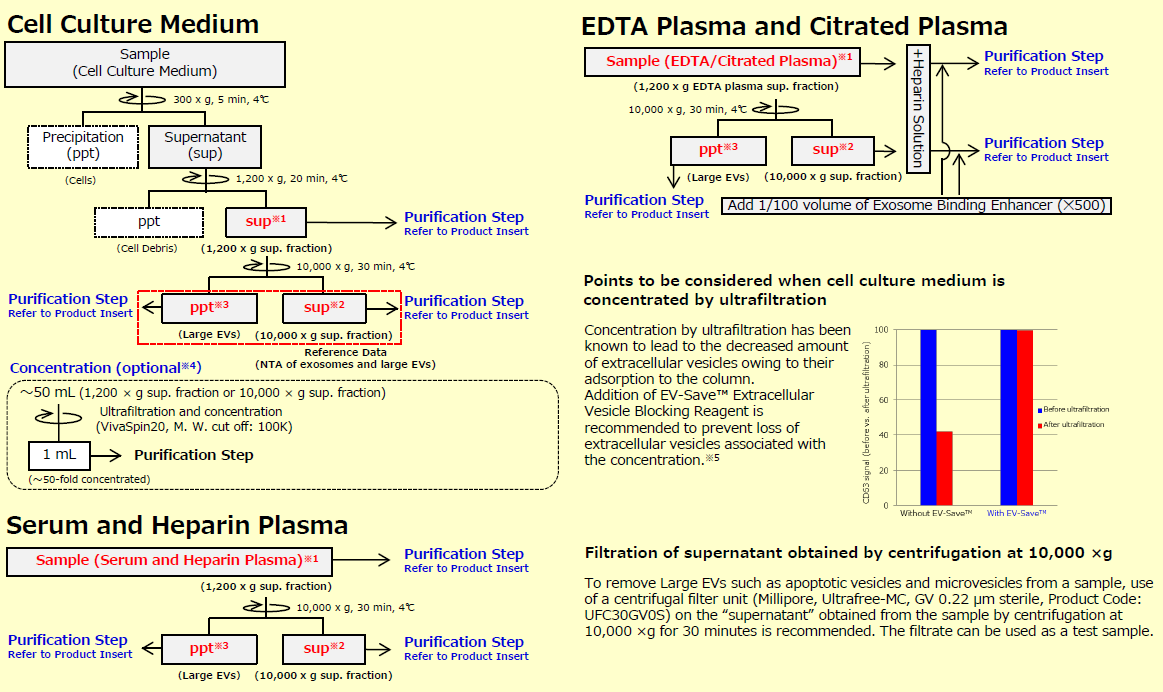
※1 When exosomes and large EVs are needed, use 1,200 x g sup. franction as sample.
※2 When exosomes are needed, use 10,000 x g sup. fraction as sample.
※3 When Large EVs are needed, use ppt of Large EVs obtained by centrifugation at 10,000 x g as sample after suspending it with TBS.
※4 The concentration step is an option when using a large volume (~ 50 mL) of cell culture supernatant as a sample for purification. However, since recovery efficiency improves, please perform it as much as possible.
※5 Because EV-Save™ contains polymers, its use is not recommended for preparation of proteomic analysis samples.
Note : a volume of large or small sample
In the case of large volume
The concentration of the sample is recommended when using a large volume (~50 mL) of cell culture supernatant as a sample for purification. Since recovery efficiency improves, please perform it as much as possible.
In the case of small volume
Add the appropriate volume of TBS into samples to reach the volume of 0.5 mL to obtain the better mixture of the Exosome Capture-immobilized beads with the sample. (Example: 100-200 μL → 500 μL)
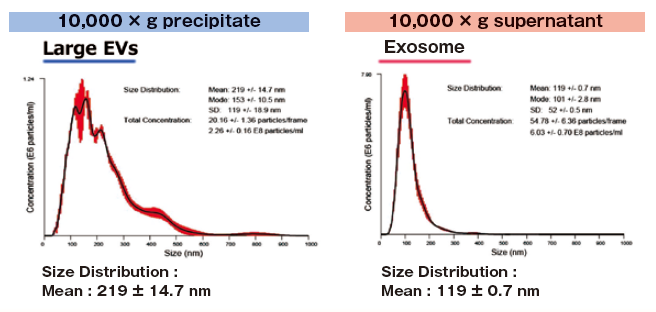
Reference data : NTA of exosomes and large EVs
1 mL of K562 cell culture supernatant (collected after stimulating exosome secretion with monensin sodium salt) was centrifuged at 10,000 x g to isolate supernatant and precipitate (suspended with 1 mL of TBS) fractions.
Then, extracellular vesicles were purified from both fractions with MagCapture™ Exosome Isolation Kit PS and analyzed using NanoSight LM10.
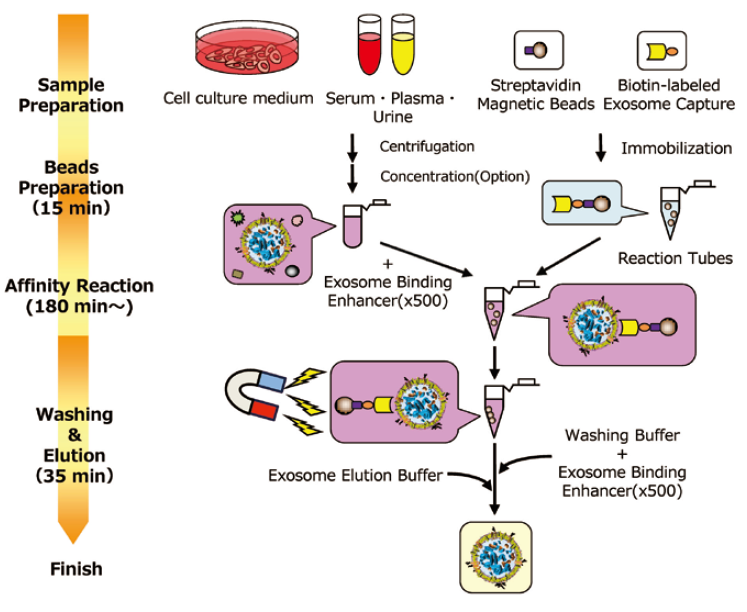
Outline of Procedure of MagCaptureTM Exosome Isolation Kit PS
Analysis
Analysis of extracellular vesicles purified from serum / plasma / urine samples
Comparing the yield of exosomes isolated from human normal serum
Exosomes were isolated from normal human serum by using MagCapture™, ultracentrifugation and affinity method with antibody against surface antigen of exosome, followed by Western Blot with the anti-CD9 and anti-CD63 antibodies.
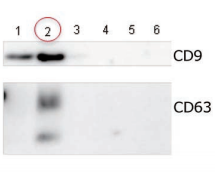 |
Lane 1: Ultracentrifugation Lane 2: MagCapture™ Lane 3: Exosome Isolation reagent with antibody against CD9 [Supplier A] Lane 4: Exosome Isolation reagent with antibody against CD63 [Supplier A] Lane 5: Exosome Isolation reagent with antibody against CD81 [Supplier A] Lane 6: Exosome Isolation reagent with antibodies [Supplier A] (antibody beads-mixture of CD9, CD63, CD81 & EpCAM) |
Detection antibodyAnti-CD9 rabbit pAb, System BioscienceAnti-CD63 rabbit pAb, System Bioscience About data of WBEach signal corresponds to 150μL of the serum sample. 15μL of eluate and 5μL of 4×SDS sample buffer were mixed and applied all in each well. |
The yield of exosomes by MagCapture™ is higher than ultracentrifugation and the antibody-based method.
Isolating exosomes from human EDTA-plasma
Exosomes were isolated from EDTA-plasma, EDTA-plasma (buffer-exchanged), and serum by using MagCapture™, followed by Western Blot with the anti-Flotillin-2 antibody.
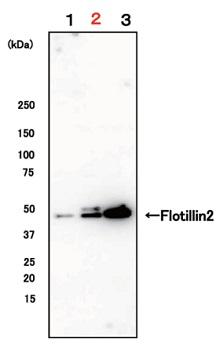 |
Lane 1: EDTA-plasma Lane 2: EDTA-plasma (buffer-exchanged) Lane 3: Serum |
Detection antibodyAnti-Flotillin-2 mouse mAb (29/Flotillin-2), BD BioscienceSample volume1 mL eachAbout data of WBEach signal corresponds to 150μL of various samples. 15μL of eluate and 5μL of 4×SDS sample buffer were mixed and applied all in each well. |
By exchanging buffer by ultrafiltration, exosomes can be isolated more efficiently.
Comparing the yield of exosomes isolated from human normal urine
Exosomes were isolated from normal human urine by using MagCapture™, ultracentrifugation and polymerbased precipitation, followed by Western Blot with the anti-CD9 antibody.
Comparison of recovery amount of marker protein
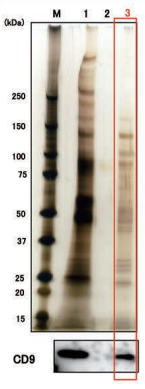 |
Lane 1: Polymer-based precipitation Lane 2: Ultracentrifugation Lane 3:Mag Capture™ |
Detection antibodyAnti-CD9 rabbit pAb, System BioscienceSample volume1 mL eachAbout data of WBEach signal corresponds to 150μL of the urine sample. 15μL of eluate and 5μL of 4×SDS sample buffer were mixed and applied all in each well. |
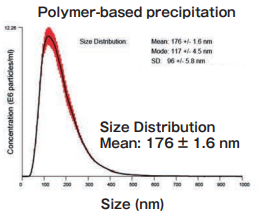
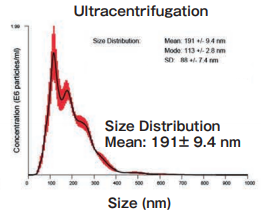
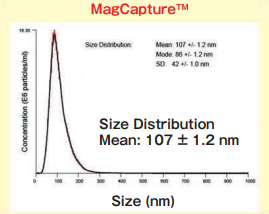
Comparison of NTA
 |
 |
 |
||
Size DistributionMean: 176 +/- 1.6 nmMode: 117 +/- 4.5 nm SD: 96 +/- 5.8 nm |
Size DistributionMean: 191 +/- 9.4 nmMode: 113 +/- 2.8 nm SD: 88 +/- 7.4 nm |
Size DistributionMean: 107 +/- 1.2 nmMode: 86 +/- 1.2 nm SD: 42 +/- 1.0 nm |
High purity exosomes can be isolated from urine sample.
Analysis of extracellular vesicles purified from culture supernatant samples
The yield and purity were compared for exosomes isolated from K562 (human chronic mylogenous leukemia: CML) cell culture supernatants (serum-free medium, or 10% Exosome-depleted FBS medium) by using MagCapture™, ultracentrifugation and polymer-based precipitation method.
MagCapture™ Exosome Isolation Kit PS
Exosomes were recovered from 1 mL of pretreated (10,000×g, 30 min.) cell culture supernatant of K562 cells (serum-free medium or 10% exosome-depleted FBS ※ 1 included medium) by using PS affinity method's standard protocol (reaction time: 3 hours)
Ultracentrifugation
10 mL of pretreated (10,000×g, 30 min.) cell culture supernatant of K562 cells (serum-free medium or 10% exosome-depleted FBS ※ 1 included medium) were ultracentrifuged at 110,000×g, 70 min., and the precipitates were suspended with TBS. Then, the suspension was ultracentrifuged again and the precipitated pellet was recovered as exosome sample.
Polymer-based precipitation
Exosomes were collected from 1 mL of pretreated (10,000×g, 30 min.) cell culture supernatant of K562 cells (serum-free medium or 10% exosome-depleted FBS※1 included medium) by Supplier A’s product in accordance with manual (Precipitation time: overnight).
※1: Centrifuged for 2 hours at 110,000 × g, and the supernatant was collected so as not to take up the precipitate.
Electron microscopic analysis and Nano analysis of isolated exosomes
The particle size of exosomes from K562 cell culture supernatant (serum-free medium) using MagCapture™, ultracentrifugation and polymer-based precipitation, respectively was determined by using NanoSight LM-10. The collected exosomes (2-4 x 1010 particles) were fixed by 2% paraformaldehyde and analyzed by electron microscopy.
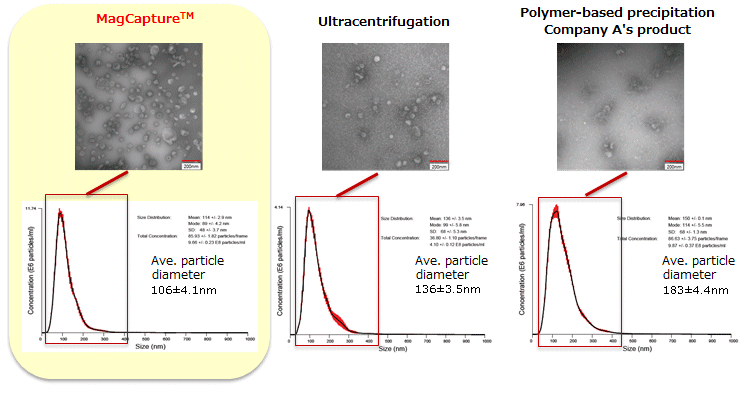
Electron microscope images were provided by Dr. R. Hanayama at Graduate School of Medicine, Kanazawa University and Dr. Nakai at iFReC, Osaka University.
MagCapture™ collected many particles around 50-100 nm in size. With electron microscopy, numerous extracellular vesicles can be seen.
Comparing the recovery amount and purity of exosomes (serum-free)
Exosomes were collected from cell culture supernatant of K562 cells (serum-free medium) by MagCapture™, ultracentrifugation and polymer-based precipitation. The recovery amount and purity were analyzed by silver staining and Western Blot with anti-CD63, anti-Flotillin-2, and anti-Lamp-1 antibodies.
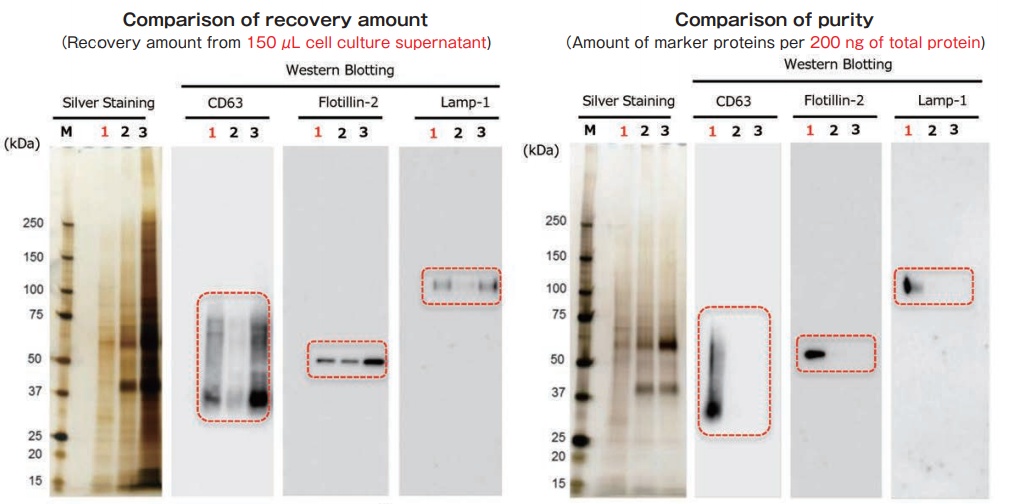
With MagCapture™, the recovery performance of exosomes is excellent and the amount of contaminant of proteins is very low, thus the balance of purity and recovery amount is the best.
Comparing the recovery amount and purity of exosomes (10% exosome-depleted FBS)
The exosomes were collected from cell culture supernatant of K562 cells (10% exosome-depleted FBS included medium) by MagCapture™, ultracentrifugation and polymer-based precipitation. The recovery amount and purity were analyzed by silver staining and Western Blot with anti-CD63, anti-Lamp-1, and anti-Flotillin-2 antibodies. Furthermore, collected samples by each method were analyzed by mass spectrometry and compared the percentage of human-derived peptides from K562 cells.
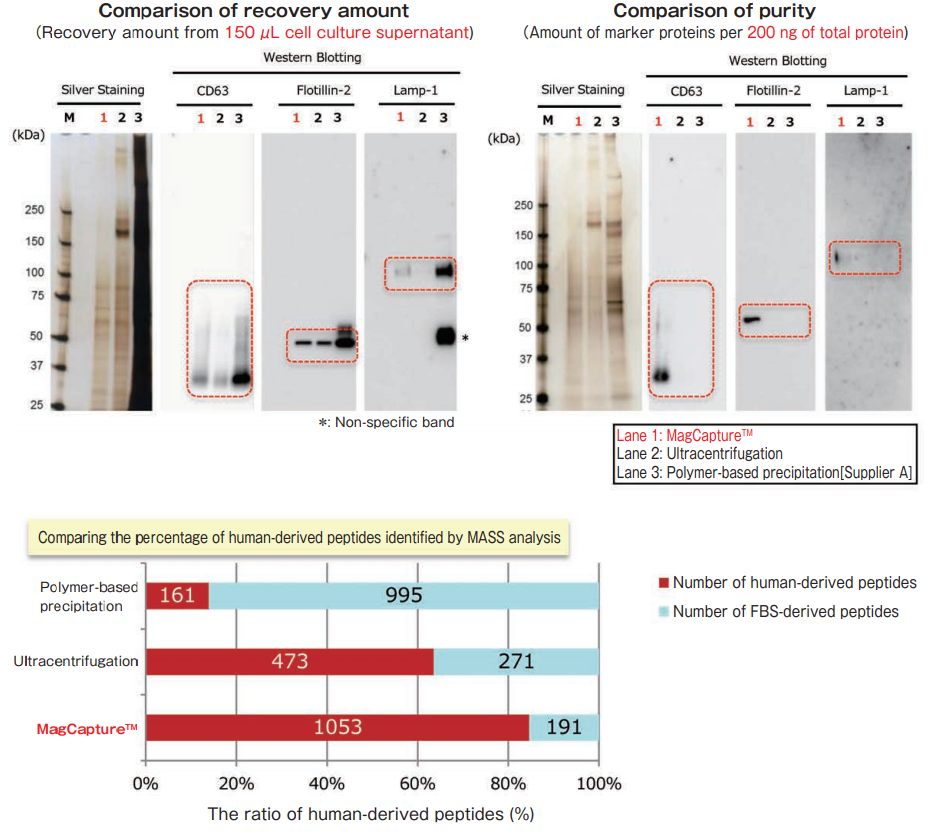
MASS analysis data was provided by Dr. R. Hanayama at Graduate School of Medicine, Kanazawa University and Dr. W. Nakai at iFReC Osaka University.
With MagCapture™, high purity exosomes are recovered even from culture medium with FBS, thus MASS analysis can be done with low background.
Comparison
Comparison of microRNA and mRNA recovery amount from exosomes derived from normal human serum
Comparison of microRNA and mRNA recovery amount from exosomes prepared by different techniques
After isolation of exosomes from normal human serum samples by ultracentrifugation and the PS affinity method, RNA was recovered using microRNA Extractor SP Kit (Code No. 295-71701). microRNA (let-7a, miR-16, miR-92a, miR-142-3p) and mRNA (GAPDH, PIK3CB) were determined by quantitative PCR and compared it using Ct values.
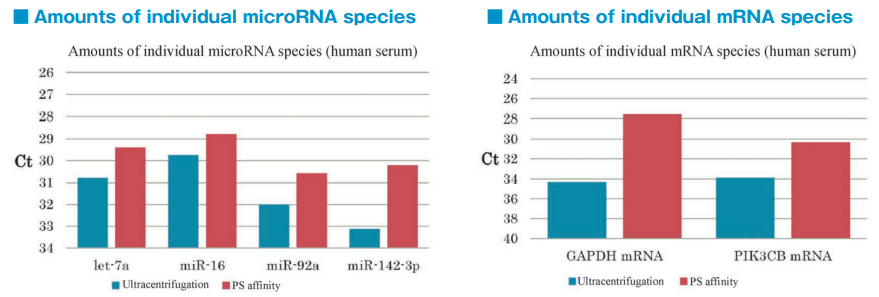
microRNA and mRNA were recovered more efficiently from exosomes isolated by the PS affinity method than those isolated by ultracentrifugation.
Comparison of RNA extraction methods from the PS affinity fractions
After isolation of exosomes from normal human serum samples by the PS affinity method, RNA was recovered using microRNA Extractor SP Kit (Code No. 295-71701) or acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenolchloroform extraction (AGPC method). microRNA (let-7a, miR-16, miR-92a, miR-142-3p) and mRNA (GAPDH, PIK3CB) were determined by quantitative PCR and compared it using Ct values.
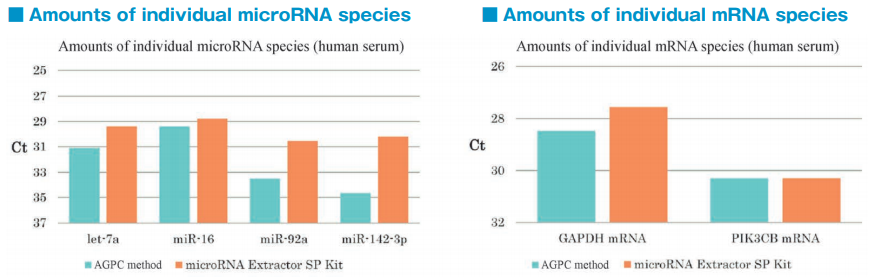
microRNA and mRNA were recovered more efficiently from exosomes using microRNA Extractor SP Kit than using AGPC method.
Proteomic Analysis of Exosomes
Description and results of experiment
Exosomes were purified from K562 cell culture supernatant containing 10% exosome-free FBS using either the PS affinity method, ultracentrifugation, or polymer precipitation. The obtained exosome samples were separated by 10% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and the individual whole protein bands were cut out. After in-gel digestion, proteins were identified by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS). Proteins identified in exosome preparations purified by the 3 different methods (n=3 for each method) were also compared for Pair-wise correlations.
Comparison of the top 10 proteins identified by MASS analysis
White columns: human protein derived from EVs
Gray columns: bovine protein contaminants derived from FBS
Red color: marker proteins of EVs
Sample: K562 cell culture Sup. (10% exosome-depleted FBS included)
| PS Affinity | Ultracentrifugation | Polymer Precipitation | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Heat shock cognate 71 kDa Protein | DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit | Complement C3 |
| 2 | Annexin A6 | Transferrin receptor protein 1 | Alpha-2-macroglobulin |
| 3 | Transferrin receptor protein 1 | Serum albumin | Fibronectin |
| 4 | V-type proton ATPase catalytic subunit A | ATP-dependent RNA helicase A | Serum albumin |
| 5 | Flotiillin-2 | Tubulin beta-5 chain | Thrombospondin-1 |
| 6 | Programmed cell death 6-interacting protein | Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein | Complement C4 |
| 7 | 4F2 cell-surface antigen heavy chain | Fatty acid synthase | Alpha-1-antiproteinase |
| 8 | Annexin A1 | 4F2 cell-surface antigen heavy chain | Apolipoprotein B-100 |
| 9 | Kinase D-interacting substrate of 220 kDa | U5 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein helicase | Hemoglobin fetal subunit beta |
| 10 | Annexin A2 | Tubulin beta-4B chain | Tubulin beta-5 chain |
While proteins of bovine serum origin are present in the greater amount of exosome preparations obtained by polymer precipitation, more exosome marker proteins are identified in exosome preparations obtained by the PS affinity method.
Comparison of Pair-wise correlation
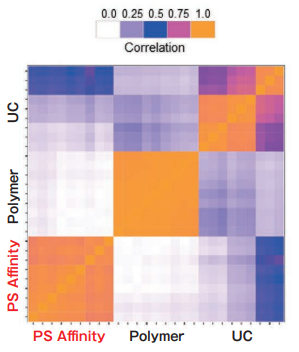
Sample: K562 cell culture Sup. (10% exosome-depleted FBS included)
| Reproducibility | |
|---|---|
| Ultracentrifugation (UC) | △ |
| Polymer Precipitation | ○ |
| PS Affinity | ○ |
Reference: Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 23;6:33935. Nakai W et al.
Polymer precipitation and the PS affinity method exhibit high intra-method correlation, while the intra-method correlation for ultracentrifugation is a little bit lower. Inter-method correlations between different methods are relatively low. The different purification methods might yield different exosome populations.
Assay of protein concentration
Assay of protein concentration in exosomes using Protein Assay BCA Kit
PProtein Assay BCA Kit, capable of assaying total protein concentration in solution using bicinchoninic acid (BCA), is the most widely used protein assay kit. It is based on the principle of reduction of Cu2+ to Cu+ by protein under basic conditions. Chelate formation between Cu+ and BCA generates a purple-colored chelate. Since the purple color becomes more intense in proportion with protein concentration, the protein concentration is determined by comparing this absorbance at 562 nm with a standard curve of absorbance from varying bovine serum albumin (BSA).
Here, the protein concentration in an exosome preparation purified from cell culture supernatant using MagCapture™ Exosome Isolation Kit PS was determined according to the high-sensitivity protocol for Protein Assay BCA Kit.
Description and results of experiment
An exosome solution purified using MagCapture™ Exosome Isolation Kit PS pipetted into a 96-well plate in 25 μL aliquots and then 200μL of a mixture of Reagent A and Reagent B included in Protein Assay BCA Kit was added to each well. After subsequent incubation at 60℃ for 30 minutes, the absorbance was measured at 560 nm (Figure 1). The result demonstrated that the protein concentration in a purified exosome preparation was able to determine using the high-sensitivity protocol for Protein Assay BCA Kit.
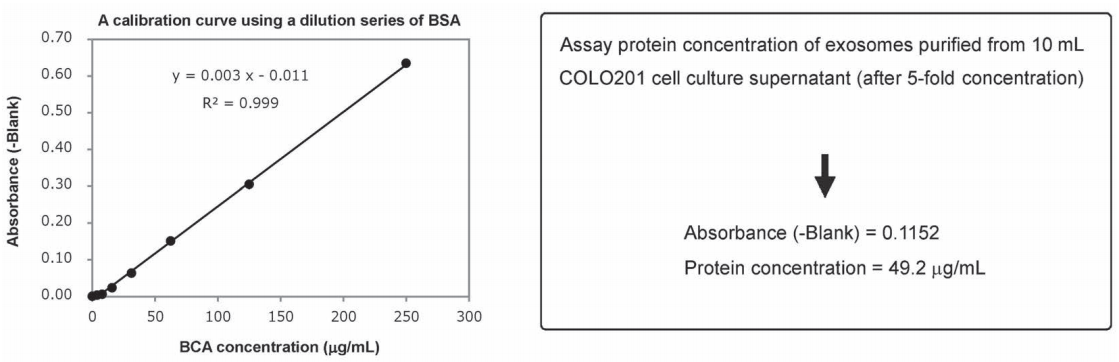
Figure 1. A BSA calibration curve determined using Protein Assay BCA Kit and assay of protein concentration of a purified exosome preparation
Overview of BCA assay protocol
Since protein concentrations of exosome preparations are rather low, use undiluted samples for BCA protein assay.
- Pipette 25μL per well of standard BSA solutions (250, 125, 62.5, 31.25, 15.625μg/mL) and a standard BLANK into a 96-well plate.
- Pipette 25μL per well of a purified exosome preparation and Elution Buffer (BLANK) on a 96-well plate.
- Add 200μL per well of a mixture of Reagent A and Reagent B (A: B=50: 1) of Protein Assay BCA Kit (Code: 297-73101) to each sample-containing well.
- Incubated the plate at 60℃ for 30 minutes.
- Allow the plate to cool at room temperature.
- Measure the absorbance at 560 nm.
Exosome labeling and uptake assay with HeLa cells
Experiment overview
Exosomes purified by MagCapture™ Exosome Isolation Kit PS were labeled with PKH67 (Sigma) and confirmed their ability to be incorporated into HeLa cells.
Exosome labeling with PKH67
- Purify exosomes using MagCapture™ Exosome Isolation Kit PS (from COLO201 cell culture supernatant on the day of experiment).
* To prevent loss of labeled samples due to adsorption in Step 6-7 Gel filtration, addition of EV-Save™ Extracellular Vesicle Blocking Reagent to the elution buffer included in the kit is recommended. Using the elution buffer containing EV-Save™, the sample can be prepared with the minimal loss. - Determine the protein concentration and particle concentration by BCA Assay and using NanoSight.
- Dispense the exosome sample solution corresponding to 3 μg protein* in a 1.5 mL tube.
* Prepare an appropriate amount as needed for the experiment. - Dissolve 2.0 μL PKH67 linker in 0.25 mL of Diluent C (provided with the PKH67 kit) - 4 x Dye solution*
* Prepare an appropriate amount as needed for the experiment. - Add 1/3 volume of 4 x Dye solution to the exosome sample, mix, and incubate the mixture at room temperature for 5-10 minutes.
- Equilibrate Exosome Spin Columns (MW 3000) (Thermo #4484449) with PBS according to the protocol provided with the product.
- Apply 100μL of each sample to each spin column equilibrated as described above* and centrifuge at 750 x for 2 minutes to separate unbound dye from labeled exosomes.
* Because the maximum loading volume is 100 μL per column, multiple columns corresponding to the sample volume are recommended to be kept on hand where the sample amount is more than 100 μL. - Add the solution containing labeled exosomes* to HeLa cells seeded on a dish on a preceding day. After 24 hours, perform microscopic observation and flow cytometry.
* Adjust the number of exosomes added.
-
Results of microscopic observation
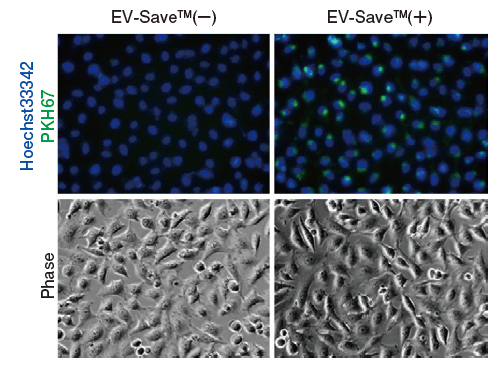
-
Results of flow cytometry
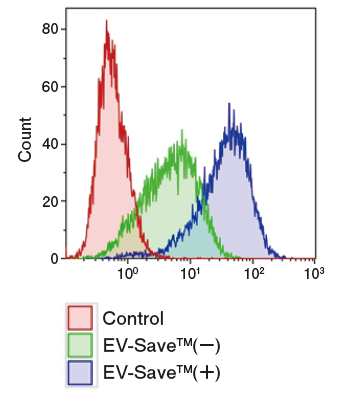
Figure 1. Observation of the uptake of PKH-labeled exosomes into HeLa cells. Exosomes were isolated from COLO201 cell conditioned medium using MagCapture™ Exosome Isolation Kit PS (total protein 3 μg, particle number 1 x 1010), followed by labeling using PKH67 Green Fluorescent Cell Linker Kit (Sigma). The uptake of the labeled exosomes into HeLa cells was confirmed by fluorescence microscopy (left) and flow cytometry (right).
Now you can see that PKH67-labeled exosomes are incorporated th rough endocytosis in both microscopy image and flow cytometry chart. Also, you can find that EV-Save™ Extracellular Vesicle Blocking Reagent added to the sample remarkably reduced the loss due to adsorption to the gel filtration column in a dye-removal step.
